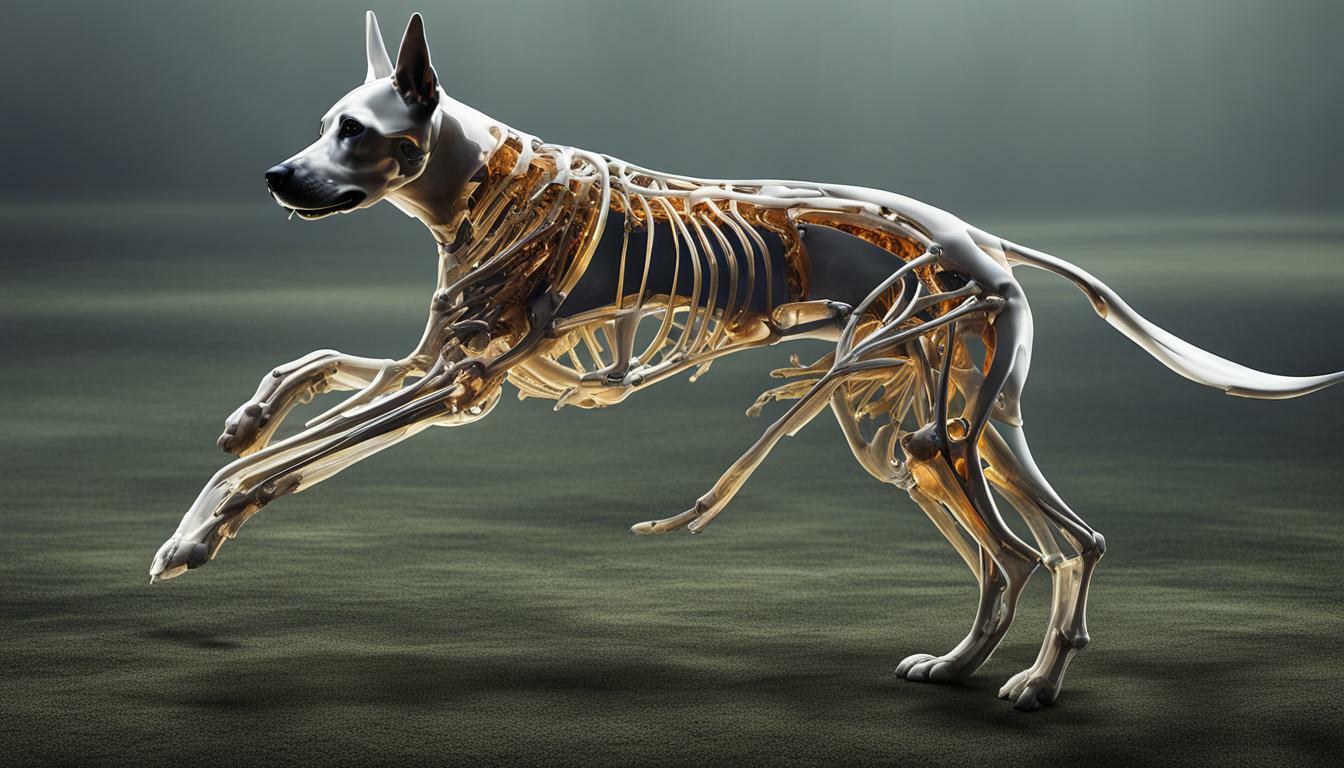
Understanding the number and structure of bones in a dog’s body is key to comprehending their anatomy and overall health. Dogs generally have around 319 bones in their body, although the exact number can vary depending on the size and breed of the dog. Puppies have more bones than adult dogs because some of their bones have not yet fused together.
The bones in a dog’s body are divided into different sections, including the skull, spine, ribcage, limbs, and tail. Dogs have a unique bone structure in their front legs that allows them to bear more weight on their forelimbs. Certain breeds of dogs are more prone to bone-related health issues such as hip dysplasia or dental problems. Bones play an important role in a dog’s overall health, and chewing on bones can promote dental health.
Dogs can suffer from bone fractures, which can be treated through immobilization or surgery. Maintaining healthy bones in dogs requires a balanced and nutritious diet, regular exercise, and proper veterinary care.
How Many Bones Does a Dog Have? Approximately 319.
- The number of bones in a dog’s body is approximately 319, varying by size and breed.
- Puppies have more bones than adult dogs, as some bones have not yet fused together.
- The bones in a dog’s body are divided into sections like the skull, spine, ribcage, limbs, and tail.
- Dogs have a unique bone structure in their front legs, enabling them to bear more weight on their forelimbs.
- Certain dog breeds are prone to bone-related health issues such as hip dysplasia or dental problems.
Canine Skeletal System: An Intricate Framework
The skeletal system in dogs is a fascinating and intricate framework, comprised of various bones that are divided into different sections, each serving a specific purpose. From the skull to the tail, each bone plays a crucial role in a dog’s overall structure and movement.
Starting with the skull, it protects the brain and sensory organs, such as the eyes and nose. The spine, consisting of individual vertebrae, supports the body and allows for flexibility. The ribcage safeguards the vital organs, including the heart and lungs, while the limbs enable dogs to walk, run, and perform various activities. The tail, consisting of several small bones called vertebrae, aids in balance and communication.
To better understand the complexity of a dog’s skeletal system, let’s take a closer look at the bone structure in the front legs. Dogs have a unique bone arrangement that allows them to bear more weight on their forelimbs. This design contributes to their agility and the ability to perform tasks such as digging, jumping, and running. Additionally, dogs’ front legs have an intricate joint system that allows for a wide range of motion, enabling them to navigate different terrains with ease.
| Bone Section | Function |
|---|---|
| Skull | Protects the brain and sensory organs |
| Spine | Supports the body and allows for flexibility |
| Ribcage | Safeguards vital organs |
| Limbs | Enables walking, running, and other activities |
| Tail | Aids in balance and communication |
Understanding the canine skeletal system is essential for dog owners and veterinarians alike. It helps us comprehend the underlying structure of dogs and provides valuable insights into their overall health and well-being.
Bones in Development: Puppies vs. Adult Dogs
The number of bones in a dog’s body can vary depending on its age, with puppies having more bones than adult dogs due to ongoing growth and development. As puppies grow, their bones go through a process called ossification, where cartilage gradually turns into bone. This process involves the fusion of certain bones, resulting in a decrease in the overall bone count as a dog reaches adulthood.
During the early stages of a puppy’s life, their bones are softer and more flexible, allowing for easier growth and movement. This flexibility also makes puppies more prone to certain types of injuries, such as fractures or dislocations. It is crucial to provide proper nutrition and a safe environment to promote healthy bone development in puppies.
As a puppy matures into an adult dog, their bones continue to strengthen and become denser. The fusion of certain bones helps form a more solid and stable skeletal structure, providing the necessary support for a dog’s body. However, it’s important to note that not all bones fuse completely, as some may remain separate throughout an adult dog’s life.
| Development Stage | Number of Bones |
|---|---|
| Puppy | Varies, generally more than in adult dogs |
| Adult Dog | Average of approximately 319 bones |
Key Differences in Bone Development:
- Puppies have more bones than adult dogs due to ongoing growth and development.
- As puppies mature, certain bones fuse together, resulting in a decrease in the overall bone count.
- While most bones fuse during growth, some bones may remain separate in adult dogs.
- Proper nutrition and a safe environment are essential for healthy bone development in puppies.
- Adult dogs have a more solid and stable skeletal structure compared to puppies.
Understanding the differences in bone development between puppies and adult dogs is crucial for pet owners and veterinarians alike. It helps provide insights into the unique needs and vulnerabilities of dogs at various stages of life. By promoting healthy bone development and providing appropriate care, we can ensure that our canine companions lead active and comfortable lives.
The Forelimb Marvel: Unique Bone Structure in Dogs
Dogs possess a fascinating bone structure in their front legs, enabling them to bear weight and engage in various activities with remarkable agility. The bones in a dog’s forelimbs are specifically designed to provide strength and flexibility, allowing them to perform tasks such as running, jumping, and digging.
The forelimbs of a dog consist of several bones that work together to support their movement. The shoulder joint connects the forelimb to the rest of the body and is made up of the scapula (shoulder blade) and the humerus (upper arm bone). These bones provide stability and allow for a wide range of motion.
Another important bone in a dog’s forelimb is the radius, which runs alongside the ulna in the lower part of the leg. These bones are responsible for the dog’s ability to rotate their paws, making it easier for them to navigate various terrains. The carpal bones, located in the dog’s wrist, connect the forelimb to the paw and provide support during weight-bearing activities.
The unique bone structure in a dog’s front legs allows them to excel in activities that require agility and strength. Whether it’s chasing a ball, leaping over obstacles, or simply walking, dogs rely on their forelimbs to perform these tasks with efficiency. Understanding the intricacies of a dog’s bone structure can help us appreciate their remarkable abilities and contribute to their overall well-being.
Bone-Related Health Issues in Dogs
Just like humans, dogs are susceptible to bone-related health issues that can affect their mobility and quality of life. Understanding these issues is crucial for dog owners to provide the necessary care and support for their furry companions.

One common bone-related health issue in dogs is hip dysplasia, which occurs when the hip joint does not develop properly. This can lead to pain, lameness, and difficulty in walking or running. Certain breeds, such as Labrador Retrievers and German Shepherds, are more prone to hip dysplasia. Regular exercise, maintaining a healthy weight, and providing joint supplements can help manage this condition.
Another significant bone-related health concern in dogs is dental problems. Poor dental hygiene can lead to gum disease, tooth decay, and even bone loss in the jaw. Chewing on bones can help clean a dog’s teeth by removing plaque and tartar buildup. However, it’s important to choose the right bones that are safe for dogs to chew on, as some bones can splinter and cause injuries.
In addition to hip dysplasia and dental problems, dogs can also suffer from fractures. Fractured bones in dogs can occur due to accidents, falls, or trauma. Treatment options for bone fractures in dogs include immobilization with splints or casts, or in severe cases, surgery may be required. Prompt veterinary care is essential to ensure proper healing and minimize the risk of complications.
Taking good care of your dog’s bones is crucial for their overall health and well-being. Providing a balanced and nutritious diet that includes essential nutrients like calcium and phosphorus is vital for maintaining strong and healthy bones. Regular exercise helps keep the bones and joints strong and flexible. Routine check-ups with a veterinarian can help detect any potential bone-related issues early on and ensure appropriate preventive measures are in place.
In conclusion, bone-related health issues can significantly impact a dog’s mobility and quality of life. Being aware of common problems like hip dysplasia, dental issues, and fractures allows dog owners to take proactive steps to prevent, manage, and treat these conditions. By providing a healthy lifestyle, regular veterinary care, and appropriate chew toys, dog owners can help keep their furry friends’ bones strong and healthy for years to come.
| Common Bone-Related Health Issues in Dogs |
|---|
| Hip dysplasia |
| Dental problems |
| Fractures |
Promoting Dental Health: The Role of Bones
Chewing on bones not only provides dogs with entertainment but also plays a significant role in promoting their dental health. When dogs chew on bones, it helps to remove plaque and tartar buildup, which can lead to gum disease and tooth decay. The mechanical action of gnawing on bones helps to scrape away bacteria and food particles, keeping their teeth and gums clean and healthy.
In addition to cleaning their teeth, chewing on bones also helps to strengthen a dog’s jaw muscles. The act of chewing provides exercise for these muscles, promoting their development and maintaining their strength. This is particularly important for certain breeds that have a predisposition to dental issues, as a strong jaw can help prevent problems such as malocclusions or misalignment of the teeth.
“Chewing on bones not only provides dogs with entertainment but also plays a significant role in promoting their dental health.”
It’s important to note that not all bones are suitable for dogs to chew on. Bones that are too small or brittle can pose a choking hazard or cause damage to their teeth. It’s best to provide your dog with specially-designed dog bones that are safe for chewing and promote dental health. These bones are typically made from durable materials that can withstand the chewing action of dogs without splintering or breaking.

By incorporating bone chewing into your dog’s dental care routine, you can help ensure their teeth and gums stay healthy and strong. Remember to always supervise your dog while they are chewing bones and consult with your veterinarian for guidance on the best types of bones for your dog’s size and breed.
Fractured Bones: Treating Injuries in Dogs
Just like humans, dogs can suffer from bone fractures, which require proper attention and care for their recovery. Whether it’s a broken leg, a fractured rib, or a cracked skull, bone injuries can cause pain and discomfort for our furry friends. Seeking veterinary assistance is crucial to ensure the best outcome for your dog’s healing process.
When it comes to treating bone fractures in dogs, there are several options depending on the severity and location of the injury. In some cases, immobilization may be sufficient to support the bone and encourage healing. This can involve the use of casts, splints, or braces to restrict movement and provide stability.
In more severe cases where the bones are significantly displaced or shattered, surgery may be necessary. During surgery, the veterinarian will realign the bones and use plates, screws, or pins to hold them together. This helps to promote proper healing and restore functionality to the affected area.
It’s important to follow the veterinarian’s instructions closely during the recovery period to ensure a successful outcome. This may involve restricting your dog’s activity, providing pain medication, and scheduling follow-up visits for X-rays to monitor the healing progress.
Understanding the proper treatment options for bone fractures in dogs is essential for their well-being. By seeking prompt veterinary care and following the recommended treatment plan, you can help your canine companion recover and get back to their happy and active selves.
Image: 
| Treatment Options | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
| Immobilization (casts, splints, braces) | – Non-invasive – Promotes natural healing – Less costly |
– Limited access for cleaning – May require prolonged immobilization |
| Surgery with internal fixation (plates, screws, pins) | – Precise realignment of bones – Provides stability for proper healing – Faster recovery in some cases |
– Invasive procedure – Higher cost – Risk of infection or implant failure |
“Proper treatment and care for bone fractures in dogs can make a significant difference in their recovery and quality of life.” – Dr. Sarah Miller, Veterinarian
Maintaining Healthy Bones in Dogs
Ensuring the well-being of a dog’s bones involves a combination of factors such as nutrition, exercise, and regular veterinary check-ups. A balanced and nutritious diet is essential for maintaining healthy bones in dogs. Incorporating high-quality dog food that is rich in essential nutrients like calcium and phosphorus can help support bone strength and growth. It’s important to consult with a veterinarian to determine the right diet and portion sizes based on your dog’s age, breed, and activity level.
Regular exercise plays a crucial role in maintaining strong and healthy bones in dogs. Activities such as walking, running, and playing fetch provide weight-bearing exercise that stimulates bone development and helps prevent bone loss. Exercise also helps to keep your dog’s muscles and joints strong, providing support to the skeletal system. However, it’s important to avoid over-exertion, particularly in puppies and older dogs, as excessive strain on the bones and joints can lead to injuries.
Veterinary check-ups are essential for monitoring your dog’s bone health. Regular visits to the vet allow for early detection and treatment of any potential bone-related issues. During these check-ups, the vet can assess your dog’s overall bone structure, identify any signs of abnormalities, and recommend appropriate interventions if necessary. They can also guide supplements or medications that may be beneficial for supporting bone health in certain dogs.
| Nutrition for Healthy Bones | Exercise for Strong Bones | Regular Veterinary Check-ups |
|---|---|---|
| Provide a balanced and nutritious diet rich in essential nutrients like calcium and phosphorus. | Incorporate regular weight-bearing exercises such as walking, running, and playing fetch. | Schedule routine check-ups with a veterinarian to monitor bone health and detect any issues early. |
| Consult with a veterinarian to determine the right diet and portion sizes based on your dog’s needs. | Avoid over-exertion to prevent injuries that can affect bone health. | Address any concerns or abnormalities promptly to ensure appropriate interventions. |
| Consider supplements or medications recommended by the vet to support bone health. | Provide mental stimulation and interactive play to keep your dog active and engaged. | Follow recommended vaccination and deworming schedules for overall health and well-being. |
“Proper nutrition, regular exercise, and veterinary care are the pillars of keeping a dog’s bones healthy. By providing a balanced diet, engaging in regular physical activity, and scheduling routine check-ups, we can help prevent bone-related issues and promote overall well-being in our furry friends.” – Dr. Sarah Thompson, DVM

- Balanced nutrition, exercise, and regular veterinary check-ups are key to maintaining healthy bones in dogs.
- A diet rich in nutrients like calcium and phosphorus supports bone strength and growth.
- Weight-bearing exercise stimulates bone development and helps prevent bone loss.
- Regular vet check-ups allow for early detection and intervention of any bone-related issues.
By prioritizing the well-being of our dogs’ bones and implementing these essential practices, we can contribute to their overall health and happiness throughout their lives.
Breed Variations: Bone Differences among Dogs
Different dog breeds exhibit variations in their bone structure, which can contribute to their distinctive physical attributes and potential health concerns. The size, shape, and density of a dog’s bones can vary greatly depending on its breed, resulting in differences in overall body structure and movement capabilities. Understanding these variations is important for breeders, veterinarians, and dog owners alike.
For example, large breed dogs such as Great Danes and Mastiffs tend to have heavier and denser bones compared to smaller breeds like Chihuahuas or Dachshunds. This is to support the increased weight and size of their bodies. The bones of large breeds may also develop at a slower rate, potentially leading to skeletal issues if proper nutrition and growth management are not provided during their formative years.
Additionally, certain breeds are predisposed to specific skeletal concerns. For instance, breeds with short legs like Dachshunds or Basset Hounds are prone to intervertebral disc disease due to the structural strain on their elongated spines. Similarly, large and giant breeds, such as the Great Dane or Newfoundland, are more susceptible to conditions like hip dysplasia, which can affect the stability and function of their hips.
| Breed | Distinctive Bone Features | Common Health Concerns |
|---|---|---|
| German Shepherd | Strong and well-developed skeleton | Hip dysplasia, elbow dysplasia |
| Greyhound | Long, slender bones for speed | Fractured metatarsals, osteosarcoma |
| Dachshund | Elongated spine, short legs | Intervertebral disc disease, patellar luxation |
It’s essential to consider these breed-specific bone differences when selecting a dog or caring for a specific breed. Proper breeding practices, including health testing and responsible selection, can help mitigate genetic skeletal issues. Regular veterinary check-ups and early intervention are crucial for identifying and managing any potential bone-related health concerns in dogs of all breeds.
- Dogs of different breeds exhibit variations in bone structure, contributing to their physical attributes and potential health concerns.
- Large breeds have heavier and denser bones, while smaller breeds have lighter and less dense bones.
- Breed-specific bone differences can lead to breed-specific health concerns, such as hip dysplasia or intervertebral disc disease.
- Proper breeding practices, regular veterinary care, and early intervention are important for maintaining the skeletal health of dogs.

Dogs’ tails are not just fluffy appendages; they are intricately connected to their skeletal system, serving various functions through the composition of their bones. The tail is an extension of the spine and is made up of a series of small bones called vertebrae. The number of vertebrae in a dog’s tail can vary depending on the breed, but it typically ranges from 5 to 23.
The bone structure of a dog’s tail allows for flexibility and mobility. Each vertebra is connected by ligaments and muscles, enabling the tail to move in different directions. This flexibility is essential for dogs as they use their tails for balance, communication, and expressing emotions.
Some dog breeds have naturally long tails, while others have naturally short or docked tails. The length of a dog’s tail is determined by genetics and serves different purposes. Dogs with long tails can use them as a counterbalance while navigating uneven terrain or making sharp turns. On the other hand, dogs with short or docked tails have reduced tail mobility but can still communicate through other body language cues.

| Breed | Tail Length | Tail Function |
|---|---|---|
| Golden Retriever | Long | Balance, swimming |
| Bulldog | Short | Communication |
| Poodle | Long | Expression, agility |
The bone composition of a dog’s tail is primarily made up of cartilage and connective tissue. This composition allows for a balance between flexibility and strength. The cartilage provides elasticity, allowing the tail to bend and twist, while the connective tissue provides support and stability.
Understanding the bone composition of a dog’s tail helps us appreciate the importance of this appendage in their overall well-being. It serves as a communication tool, an expression of emotions, and a means of maintaining balance. So, the next time you see a dog wagging its tail, remember that it’s not just a wag of happiness but a complex interaction of bones signaling their emotions.
The Role of Nutrition in Bone Health
A well-balanced and nutritious diet is key to supporting and maintaining healthy bones in dogs throughout their lives. Proper nutrition provides the essential nutrients necessary for bone growth, development, and maintenance. Dogs require a diet that is rich in calcium, phosphorus, and vitamin D, as these nutrients play a crucial role in bone health.
Calcium is the most abundant mineral in the body and is essential for the formation and strength of bones. It helps in the development of a strong skeletal system and aids in muscle function and nerve transmission. Phosphorus works in tandem with calcium to promote healthy bone growth and repair. Vitamin D plays a vital role in the absorption of calcium and phosphorus from the intestines. It also helps regulate the levels of these minerals in the blood.
A balanced diet should include high-quality dog food that is specifically formulated to meet the nutritional needs of dogs. It is important to choose food that is appropriate for the dog’s age, size, and breed. Puppies require a diet that supports their rapid growth and development, while adult dogs need a diet that maintains their bone health. Consulting with a veterinarian can help determine the best diet plan for a dog based on their individual needs.
| Nutrient | Recommended Daily Intake | Sources |
|---|---|---|
| Calcium | 1,000 – 1,500 mg | Dairy products, fish, leafy green vegetables |
| Phosphorus | 800 – 1,200 mg | Meat, fish, poultry, whole grains |
| Vitamin D | 400 – 1,000 IU | Fatty fish, egg yolks, fortified dairy products |
Proper nutrition is essential for maintaining healthy bones in dogs. A well-balanced diet that provides adequate amounts of calcium, phosphorus, and vitamin D is crucial for bone growth, development, and maintenance. Consult with a veterinarian to ensure that your dog’s diet meets their specific nutritional needs.
In addition to a nutritious diet, regular exercise is also important for maintaining strong and healthy bones in dogs. Physical activity helps stimulate bone growth and maintain bone density. It is important to provide dogs with regular opportunities for exercise, such as daily walks, playtime, and interactive toys. However, it is essential to consider the dog’s age, breed, and any underlying health conditions when determining the appropriate level of exercise.

By providing a well-balanced diet and regular exercise, dog owners can contribute to the overall bone health and well-being of their furry companions. Remember, a healthy dog is a happy dog!
Concluding Thoughts on Dog Bones
Understanding the intricacies of a dog’s skeletal system and the role of bones is essential for every dog owner, ensuring the best possible care and support for their canine companions. Dogs generally have around 319 bones in their body, although the exact number can vary depending on the size and breed of the dog. Puppies have more bones than adult dogs because some of their bones have not yet fused together.
The bones in a dog’s body are divided into different sections, including the skull, spine, ribcage, limbs, and tail. This intricate framework provides support, and protection, and enables various movements. Dogs have a unique bone structure in their front legs, allowing them to bear more weight on their forelimbs and enhancing their agility.
Bone-related health issues can affect dogs, with certain breeds being more prone to conditions such as hip dysplasia or dental problems. Bones play a crucial role in a dog’s overall health, and chewing on bones can promote dental hygiene by reducing plaque buildup and maintaining strong teeth and gums.
In some instances, dogs may experience bone fractures, which require proper treatment. Depending on the severity, fractures can be managed through immobilization techniques or surgical intervention, ensuring proper healing and restoration of mobility.
Maintaining healthy bones in dogs requires a balanced and nutritious diet, providing the necessary nutrients like calcium and phosphorus. Regular exercise helps strengthen muscles attached to the bones and promotes overall bone health. It is also important to schedule regular veterinary check-ups to detect and address any potential bone-related issues early on.
By understanding and caring for our dogs’ skeletal systems and bones, we can ensure their well-being and provide them with the support they need to lead active and healthy lives.
FAQ
How many bones does a dog have?
Dogs generally have around 319 bones in their body, although the exact number can vary depending on the size and breed of the dog.
Why do puppies have more bones than adult dogs?
Puppies have more bones than adult dogs because some of their bones have not yet fused together.
What sections are the bones in a dog’s body divided into?
The bones in a dog’s body are divided into different sections, including the skull, spine, ribcage, limbs, and tail.
How does the unique bone structure in a dog’s front legs work?
The unique bone structure in a dog’s front legs allows them to bear more weight on their forelimbs, contributing to their overall movement.
What are some bone-related health issues that dogs may face?
Dogs can face bone-related health issues such as hip dysplasia and dental problems, which can impact their overall well-being.
How do bones promote dental health in dogs?
Chewing on bones can help maintain strong teeth and gums, promoting dental health in dogs.
How are bone fractures in dogs treated?
Bone fractures in dogs can be treated through immobilization or surgery, depending on the severity of the fracture.
What can I do to maintain healthy bones in my dog?
Maintaining healthy bones in dogs requires a balanced and nutritious diet, regular exercise, and proper veterinary care.
Are there any variations in bone structure among different dog breeds?
Yes, different dog breeds may have variations in their bone structure, which can result in specific characteristics or predispositions.
What is the bone composition of a dog’s tail?
A dog’s tail is composed of bones that contribute to its mobility and communication abilities.
How does nutrition affect bone health in dogs?
Nutrition plays a crucial role in maintaining optimal bone health in dogs, with nutrients such as calcium and phosphorus being essential.






